Hydrogen Water Nanostrings and Quantum Coherence Phenomena
Further reading: https://nanostrings.org/
Hydrogen Water Nanostrings and Coherence
Hydrogen water nanostrings refer to nanoscale structures where hydrogen atoms are integrated into water molecules. These structures can exhibit quantum coherence, where the hydrogen atoms maintain a stable quantum state over time. This coherence is essential for understanding the unique properties of water at the nanoscale, including its behavior in confined spaces and its interaction with other molecules. Quantum coherence in hydrogen water nanostrings can influence various physical and chemical processes, making it a significant area of study in nanotechnology and materials science [1].
Introduction: Hydrogen water
Hydrogen water, characterized by its high concentration of molecular hydrogen (H₂) dissolved in water, has garnered increasing interest for its potential therapeutic effects due to its antioxidant properties. In recent years, research has extended beyond the biochemical implications of hydrogen water to its possible quantum mechanical properties, particularly in the context of nanostructures and coherence phenomena. This report explores the relationship between hydrogen water nanostrings, quantum coherence, and noise generation, shedding light on the intersection of chemistry, nanotechnology, and quantum physics.
Data Analysis Challenges in Nanotechnology
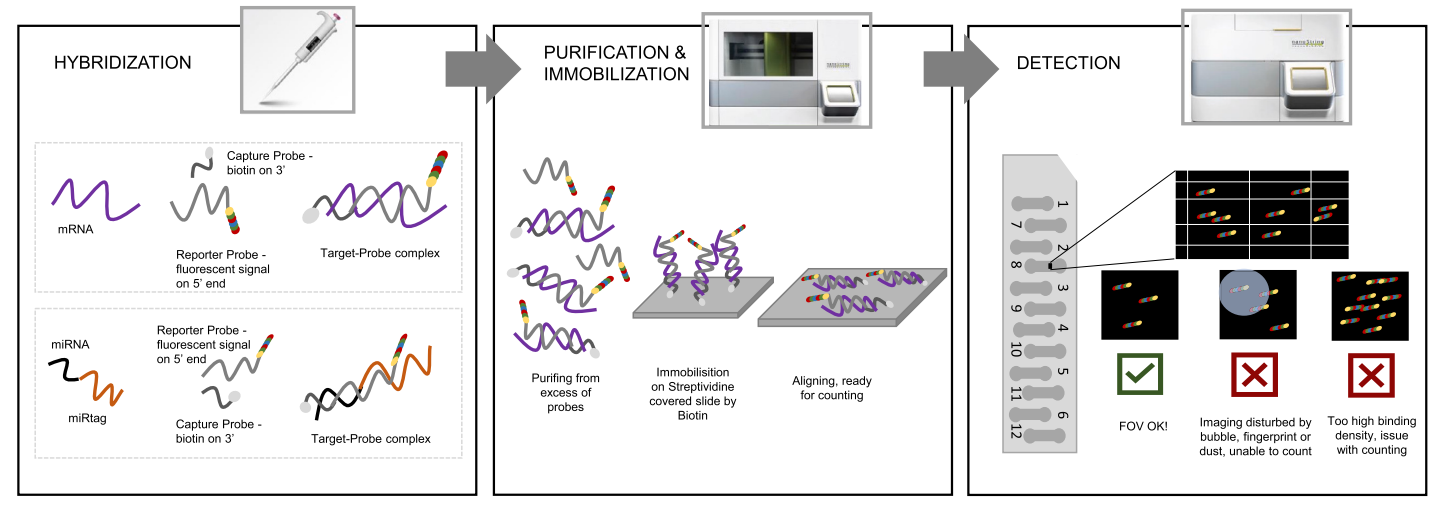
Data analysis in nanotechnology often faces challenges due to the variability and noise inherent in the system. Similar to how the NanoString nCounter platform has developed specific workflows to mitigate noise and improve data accuracy, analyzing hydrogen water nanostrings requires a robust approach to manage quantum-level variability. Effective data pre-processing, normalization, and quality control are essential for ensuring that the quantum properties, such as coherence and entanglement, are accurately captured and interpreted. Drawing parallels from nCounter’s advanced data workflows could guide better experimental protocols and analytical methods for hydrogen water research, allowing clearer insights into the quantum mechanical properties of these systems [2].
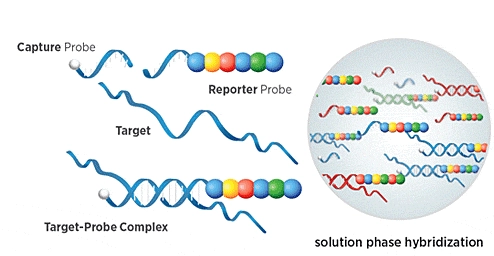
BioXpedia’s laboratories offer gene expression profiling using NanoString nCounter panels. NanoString is a robust technology that works across a wide range of sample types, including FFPE tissue sections. It allows for direct, digital detection without amplification, providing precise quantification of target molecules. This technology is highly suitable for analyzing complex biological systems, including nanostructured hydrogen water, due to its minimal bias and reliability.
Hydrogen Water Nanostrings: Structure and Properties
Nanostrings refer to nanoscopic, string-like structures within materials, and in the context of hydrogen water, these structures can emerge from the interactions between dissolved hydrogen and water molecules at the nanoscale. Nanostructuring water with dissolved hydrogen may potentially enhance the interaction of hydrogen molecules with the surrounding water matrix, stabilizing these structures. The unique behavior of hydrogen water at the nanoscale can contribute to its therapeutic efficacy.
Molecular hydrogen exhibits several unique quantum properties, including superposition, coherence, and tunneling effects, which become more pronounced in nanostructured environments. In water nanostrings, the dissolved hydrogen can maintain a delicate balance of quantum coherence, where the phase relationships between hydrogen molecules remain consistent, leading to coherent states. These states allow for potential quantum phenomena, including energy transfer and quantum entanglement, which may explain certain unexplained biological effects reported in hydrogen water therapies.
Quantum Coherence in Hydrogen Water Nanostrings
Quantum coherence refers to the phenomenon where particles, such as electrons or hydrogen molecules, exhibit wave-like properties that allow them to interact in an orderly and synchronized fashion. In hydrogen water nanostrings, quantum coherence may manifest through the alignment of water dipoles, induced by hydrogen bonding and the nanostructured environment. This coherence is thought to play a role in facilitating more efficient energy transfer within the system, which could have implications for bioenergetic processes.
In biological systems, quantum coherence has been hypothesized to contribute to processes such as photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Similarly, in hydrogen water nanostrings, the coherent state of hydrogen molecules might enhance the efficiency of redox reactions in cells, aiding in the neutralization of free radicals and reducing oxidative stress. This suggests that hydrogen water, particularly in its nanostructured form, could have novel biological effects that arise from quantum mechanical properties.
Quantum Coherent Domains
Water molecules can form quantum coherent domains, where they oscillate between different energy states. These domains are created through the interaction of light with liquid water, leading to a collective behavior of water molecules. This collective behavior is essential for many biological functions, as it allows for efficient energy transfer and precise coordination at the molecular level [2].
Quantum Phenomena in Nanostrings: Implications for Hydrogen Water
Quantum phenomena such as tunneling, entanglement, and decoherence can occur in hydrogen water nanostrings, where hydrogen molecules experience quantum effects due to the confined environment. These effects may enhance the solubility and stability of hydrogen within the water, creating a highly active form of molecular hydrogen. Quantum tunneling allows hydrogen molecules to pass through energy barriers that would typically be insurmountable, potentially increasing their ability to interact with biomolecules at the cellular level.
Entanglement, another quantum phenomenon, might enable hydrogen molecules to form entangled states, which could propagate coherent signals across the hydrogen water solution. This could lead to highly efficient energy transfer and molecular interactions, further supporting the therapeutic potential of hydrogen water.
Water Quantum Noise Generators and Hydrogen Water
Water, due to its molecular structure and dynamic hydrogen-bonding network, can act as a natural quantum noise generator. Quantum noise refers to the intrinsic fluctuations that occur in quantum systems, and in the case of water, these fluctuations arise from the constant reconfiguration of hydrogen bonds. In hydrogen water, where dissolved hydrogen is integrated into the water’s matrix, the quantum noise generated may be modulated by the presence of hydrogen nanostrings.
Quantum noise generators based on water could have practical applications in fields such as random number generation and cryptography, where the inherent unpredictability of quantum fluctuations is exploited. The use of hydrogen water as a quantum noise generator introduces an additional layer of complexity, as the dissolved hydrogen molecules, influenced by quantum coherence and entanglement, could enhance the stochastic properties of the system.
One proposed application of water quantum noise generators is in the development of quantum random number generators (QRNGs). These devices harness the inherent randomness of quantum phenomena, such as the noise generated by fluctuating hydrogen bonds in water, to produce true random numbers. Hydrogen water, with its potential for enhanced coherence and quantum effects, may serve as an ideal medium for QRNGs, offering a natural and potentially tunable source of quantum noise.
Biological Implications
Quantum coherence in water is believed to play a significant role in the functioning of biological systems. For example, it enables proteins and nucleic acids to operate with high efficiency and coordination, often referred to as “quantum jazz”. This coherence is thought to be a fundamental aspect of life, influencing everything from enzyme activity to cellular communication [2].
Quantum Wave Equation
Recent research has proposed a new quantum wave equation for water molecules, highlighting their coherent and entangled nature. This equation helps explain the unique electromagnetic properties of water, which are crucial for its role in biological systems [1].
Practical Applications
Understanding quantum coherence in water has potential applications in various fields, including medicine, nanotechnology, and quantum computing. For instance, it could lead to the development of new diagnostic tools or treatments that leverage the unique properties of water at the quantum level [1].
Conclusion
Hydrogen water, when considered through the lens of quantum mechanics, exhibits fascinating properties that go beyond its conventional biochemical effects. The formation of hydrogen nanostrings in water introduces new possibilities for coherence phenomena, quantum tunneling, and entanglement, which may enhance the therapeutic potential of hydrogen water. Additionally, the quantum noise generated by the dynamic hydrogen-bonding network of water, modulated by dissolved hydrogen, opens up new applications in quantum technologies such as QRNGs.
This intersection of nanotechnology, quantum physics, and biochemistry in hydrogen water systems offers a promising area of research, with potential implications for both health therapies and advanced technological applications. Future studies will need to further elucidate the mechanisms underlying these quantum effects to fully harness their potential.
References
[1] Geesink, H. J. H., Jerman, I., & Meijer, D. K. F. (2020). Water, the cradle of life via its coherent quantum frequencies. Water, 11, 78-108
[2] Chilimoniuk, J., Erol, A., Rödiger, S., & Burdukiewicz, M. (2024). Challenges and opportunities in processing NanoString nCounter data. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 23, 1951-1958.
[2] Ho, M.-W. (2014). Illuminating Water and Life. Entropy, 16(9), 4874–4891
